Objectives:
Describe the characteristics of the Security Operating Platform
Describe the differences between single-pass architecture and parallel processing
Describe the Zero Trust security model and how it relates to traffic moving through the network
Cyber Attack Lifecycle
- Reconnaissance
- Attackers carefully plan their attacks: They identify and select targets, research them. Using phishing tatics or data mining from a social media platform or company website. Company networks are scanned on this stage to look for vulnerabilities, services, and applications that can be exploited.
- Weaponisation
- Attackers determine the methods that will be used to deliver the malicious payloads to achieve their objective. The malicious payload could be present in an website, or specially crafted packages to attract the victim.
- Delivery
- The attackers may also choose to e-mail a PDF or word document.
- Exploitation
- The attacker now deploys the exploit against the vulnerabler application or system. Using the exploit kit or weaponised document. The deployment of this explot gives the attacker an initial entry point into the targeted network.
- Installation
- With initial access, attackers will try to establish a escalated privileges to gain control of the system. This will also allow the attacker to try gain a perisistent entry point into the network for future access.
- Command and Control
- The attackers establish a command channel back to a specific attacker control server, to allow communication back and forth between their own infrastricture and the infected devices
- Act on the objective
- The attacker has a persistent ongoing connection into the network. They can now act upon their motivations to try achieve their goal. Motivations could be data exfiltration, destruction of critical infrastructure or defacing web property.
Network Security Platform
The Palo Alto Networks Security Platform has three objectives:
Prevention-Focused Architecture – React only to the threats that are critically important
Highly Automated – Reduce or remove manual response
Safely enables all applications – Granular use of controls and prevention of known and unknown cyberthreats
Security Operating Platform
Cortex
Apps can be created and developed on a common application framework, known as Cortex, to rapidly build and deliver cloud-based security services with no additional infrastructure or on-premises hardware changes. Apps are delivered from the cloud to extend the capabilities of the platform, including the ability to effortlessly collaborate between apps, share threat context and intelligence, and drive automated resposne and enforcement
Contains Coretex Data Lake, and Cortex XDR
Network Security
Palo Alto Networks Security Operating Platform firewalls are designed to safely enable applications and prevent modern threats. The firewall can identify all network traffic based on applications, users, content, and devices, and lets you express your business policies in the form of easy-to-understand security rules.
Advanced Endpoint Protection
Traps Advanced Endpoint Protection providfes multi-method prevention, a proprietary combination of malware and exploit prevention methods that pre-emptively block both known and unknown threats directly on an endpoint
Cloud Security
The Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewall is a virtualised form of the Palo Alto Networks Security Operating Platform firewall. The VM-Series firewalls are designed for use in a virtualised or cloud environment to identify all network traffic based on applications,u sers, content, and devices
Additional Palo Alto Products
Panorama – Allows consolidated policy creation and centralised management. Allows for the implementation and control of firewalls centrally with an efficient rulesbase, adds insight into network-wide traffics and threats across multiple firewalls
Prisma Software as a Service – Protects cloud based applicatinos such as Box, Salesforce, and Dropbox by managing permissinobs and scanning files for external exposure and sensitive information. Prisma SaaS is focused on data loss prevention for personally identifiable information, payment card industry information and other sensitive data.
GlobalProtect – Safeguards the mobile workforce by inspecting all traffic using the organisations next generation Palo Alto firewalls deployed as internet gateways. Devices with the GlobalProtect app establish a secure SSL/VPN connection to the firewall with the best performance for a given location. Proves the organisation with full visibility of all network traffic.
AutoFocus – Gives security operatiyons and analysis teams direct access to all the threat intelligence Palo Alto networks gathers from customers, open source feeds, and the Unit 42 threat research team.
This allows security teams to focus their effects on the most important attacks and understand the most critical elements of those attacks.
Next Generation Firewall Architecture
The firewall allows you specifiy security policies based on identifcation of applications seeking access to the network.
This is different to traditional firewalls that seek to identify applications via their protocol and port number.
The next generation firewall uses packet inspection and a library of application signatures to distinguish between applications that use the same protocol and port number. With this technology the next generation firewall can identify malware applications that may use common port numbers
The Single Pass Architecture
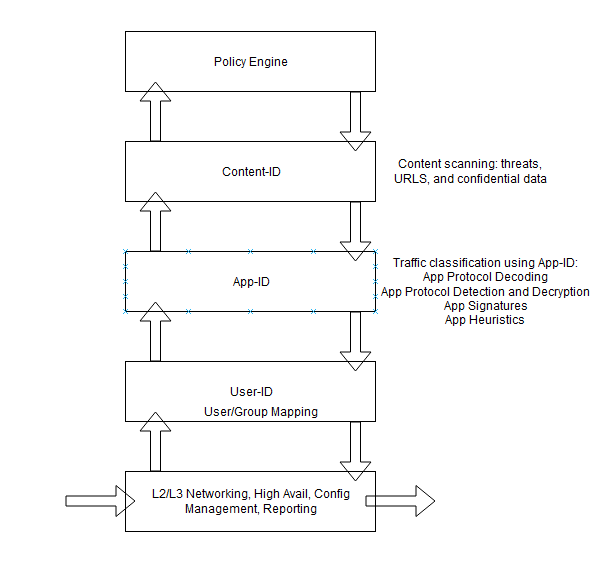
The Palo Alto firewall has a strength in it’s single pass parallell processing (SP3) engine. Each protection feature uses the same stream based signature format. This means the firewall can check for all risks that could be present in packets simultaneously.
An advantage of this simultaneous scanning is traffic can cross the Palo Alto firewall and be scanned with a minimal amount of packet buffering. This allows these advanced features to be enabled without slowing down the performance of the firewall.
The Firewall Architecture
The Palo Alto firewall has processors dedicated to specific security functions, that all work in parallel. These security functions can be be implemented in hardware offloading or software. The hardware offloading components types and capacities will vary on the specification of the firewall model.
Data Plane Processing:
- Signature Matching Components (Single pass pattern matching), a stream based uniform signature matching technology that looks for exploits, virues, spyware, credit card numbers and social security numbers with.
- Security Processing Components (Enforcing Security Policy), a multicore processor that can handle complicated tasks such as secure sockets layer (SSL decryption)
- Network Processing Components, responsible for the routing and network address translation (NAT), plus all network layer communication such as:
- Flow Control
- MAC Lookup
- Route Lookup
- Quality of Service
On the higher end hardware models, the data plane has three seperate processors that are connected via 1Gbps busses.
Control Plane Management
Contains the management parts of the firewall, responsible for management user interface for configuration, logging, and routing updates.
The higher end models of Palo Alto firewalls have their own dual core processor, RAM, and hard drive/SSD.
The Zero Trust Model
North-South traffic: Traffic that enters and leaves the network
East-West traffic: Internal traffic that never leaves the gateway
Data flows in a open network are open to a few vulnerabilities, such as a lack of visibility. If the network administrators cannot view traffic the administrators have no control of the traffic. This leaves networks open to attacks from both inside the organisation and from the public internet.
Another few examples of vulnerabilities:
Remote employees are treated as internal traffic
Wireless users, partner connections, or guests create new entry possible vulnerable entry points into the network
Remote offices need to be considered as providers of untrusted traffic because of where they are located.
Internal employees may unintentionaly present as a security threat with USB keys, or file downloads
Data flows secured by Palo Altos
The security model that Palo Altos follow is to remove the presumption of trust, known as the zero trust model.
This is an alternative security model that aims to address the shortcomings of failing permieter centric strategies by removing the assumption of trust.
Trust boundries are created taht compartmentalise different segements of the network enviroment.
Security functionality is also moved closer to different pockets of resources that require the protection needed by a firewall.
Palo Alto firewalls offer a range of threat prevention technologies that give an integrated approach against threats.
| Delivery | Exploitation | Installation | C2 | Act on the Objective | |
| App-ID | Blocked high risk applications | Block C2 communications on standard well known ports | Prevent exfiltration and lateral movement | ||
| URL Filtering | Block known malware sites | Block malware and fast flux domains | |||
| Vulnerability | Block the exploit | Prevent lateral movement | |||
| Anti-spyware | Block spyware and C2 traffic | ||||
| Anti-Virus | Block malware | Prevent lateral movement | |||
| Traps | Monitor allowed processes and executables | Prevent the exploit | Prevent malilcious .exe from running | ||
| File Blocking | Prevent drive by downloads | Prevent exfiltration and lateral movement | |||
| DoS and/or Zone | Prevent evasions | Prevent Denial of Service attacks | |||
| WildFire | Identify Malware | Detect unknown malware | Detect new C2 traffic |
Physical Firewall Platforms
PA-220 or PA-220R series
PA-800 Series
PA-3200 Series
PA-5200 Series
The PA-5280 firewall is similar to the PA-5260 firewall, but the PA-5280 firewall has double the data-plane memory. This means that the session capacity on the 5280 is doubled over that of the 5260
PA-7000 series – PA-7050 and PA-7080 are chassis architecture
Panorama M-200 or M-500/WF-500/600 servers
Virtual Systems
Virtual systems (vsys) are seperate, logical firewall instances within a single physical Palo Alto firewall.
Rather than multiple firewalls, service providers and enterprises can use a single pair of firewalls and enable virtual systems.
A virtual system consists of a set of physical and logical interfaces and subinterfaces, virtual routers and security zones. A deployment mode of virtual wire, layer 2, or layer 3 can be chosen. When virtual systems is enabled the following can be segmented from the other virtual systems:
- Administrator access
- Management of all policies, including:
- Security
- NAT
- Policy based forwarding
- Decryption
- Application Override
- Authentication
- Denial of Service Protection
- All objects
- Address objects
- Application groups
- Application filters
- Dynamic Block Lists
- Security Profiles
- Decryption Profiles
- Custom Objects
- User-ID
- Certificate Management
- Server Profiles
- Logging, reporting, visibility functions
The PA-3X00, PA-5X00, PA-7X00 firewalls all have support for virtual systems. The number of maximum virtual systems vary per platform.
On the PA-3×00 series firewall, a licence is required to create multiple virtual systems.

Leave a Reply